40.3 Box-Cox Power Transformations (.NET, C#, CSharp, VB, Visual Basic, F#)
Box-Cox power transformations
compute a rank-preserving transformation of data to stabilize variance
and make the data more normal. The power transformation is defined as
a continuously varying function, with respect to the power parameter
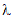 ,
,
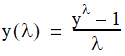
In NMath Stats,
class BoxCox compute the Box-Cox
power tranformations for a set of data points and parameter value 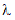 . In addition,
methods are provided for computing the corresponding log-likelihood function
and the value of
. In addition,
methods are provided for computing the corresponding log-likelihood function
and the value of 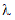 which maximizes it.
which maximizes it.
For example:
Code Example – C# Box-Cox transformations
var data = new DoubleVector( "[.15 .09 .18 .10 .05 .12 .08 .05 .08 .10 .07 .02 .01 .10 .10 .10 .02 .10 .01 .40 .10 .05 .03 .05 .15 .10 .15 .09 .08 .18 .10 .20 .11 .30 .02 .20 .20 .30 .30 .40 .30 .05]" );
var interval = new Interval( -5, 5, Interval.Type.Closed );
var bc = new BoxCox( data, interval );
Console.WriteLine( bc.Lambda );
Console.WriteLine( bc.TransformedData );
Code Example – VB Box-Cox transformations
Dim Data As New DoubleVector("[.15 .09 .18 .10 .05 .12 .08 .05 .08
.10 .07 .02 .01 .10 .10 .10 .02 .10 .01 .40 .10 .05 .03 .05 .15 .10
.15 .09 .08 .18 .10 .20 .11 .30 .02 .20 .20 .30 .30 .40 .30 .05]"
)_
Dim Interval As New Interval(-5, 5, Interval.Type.Closed)
Dim BC As New BoxCox(Data, Interval)
Console.WriteLine(BC.Lambda)
Console.WriteLine(BC.TransformedData)
BoxCox searches
from -5 to 5
until the best value of 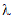 is found (the
value which maximizes the log-likelihood function).
is found (the
value which maximizes the log-likelihood function).
