35.2 Solving Differential Equations (.NET, C#, CSharp, VB, Visual Basic, F#)
Class RungeKuttaSolver
solves first order initial value differential equations by the Runge-Kutta
method. The solver computes the unknown function y
as set of tabulated values 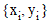 such that
such that 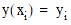 .
.
Constructing RungeKuttaSolver Instances
Instances of RungeKuttaSolver
are constructed from the number of tabulated points and a nonzero value
delta. From the number of points and
the delta, the set 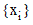 is determined as
is determined as 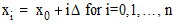 .
.
For instance:
Code Example – C# ordinary differential equations (ODE)
int n = 2000;
double delta = .001;
var solver = new RungeKuttaSolver( n, delta );
Code Example – VB ordinary differential equations (ODE)
Dim N As Integer = 2000
Dim Delta As Double = 0.001
Dim Solver As New RungeKuttaSolver(N, Delta)
Optionally, the order of the Runge-Kutta method may also be specified, using the enum RungeKutterSolver.SolverOrder.
Code Example – C# ordinary differential equations (ODE)
var solver = new RungeKuttaSolver( n, delta, SolverOrder.First );
Code Example – VB ordinary differential equations (ODE)
Dim Solver As New RungeKuttaSolver(N, Delta, SolverOrder.First)
By default, the fourth order Runge-Kutta method (RK4) is used.
Solving First Order Initial Value Problems
The Solve() method on
RungeKuttaSolver solves a given
FirstOrderInitialValueProblem
by the common Runge-Kutta method. The Solve()
method computes the unknown function y
as set of tabulated values 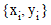 such that
such that 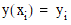 . The tabulated
values are returned either as a KeyValuePair<double[],
double[]>, or as a CenterSpace.NMath.Core.TabulatedFunction
passed by reference. (See Section 13.5
for more information on tabulated functions.)
. The tabulated
values are returned either as a KeyValuePair<double[],
double[]>, or as a CenterSpace.NMath.Core.TabulatedFunction
passed by reference. (See Section 13.5
for more information on tabulated functions.)
For example:
Code Example – C# ordinary differential equations (ODE)
KeyValuePair<double[], double[]> tabulatedValues =
solver.Solve( prob );
Code Example – VB ordinary differential equations (ODE)
Dim TabulatedValues As KeyValuePair(Of Double(), Double()) =
Solver.Solve(Prob)
or
Code Example – C# ordinary differential equations (ODE)
TabulatedFunction ftab = null;
solver.Solve( prob, ref ftab );
Code Example – VB ordinary differential equations (ODE)
Dim FTab As TabulatedFunction = Nothing
Solver.Solve(Prob, FTab)
Similarly, in the following code, results are returned as a LinearSpline, a subclass of TabulatedFunction that provides linear interpolation between tabulated values:
Code Example – C# ordinary differential equations (ODE)
var spline = new LinearSpline();
solver.Solve( prob, ref spline );
Code Example – VB ordinary differential equations (ODE)
Dim Spline As New LinearSpline()
Solver.Solve(Prob, Spline)
